Life Quality Index - Measuring Walkability in Budapest
Network-based Life Quality Index measuring urban walkability and access to amenities for the municipality of Budapest. Visualizes neighborhood-level inequalities to support targeted policy interventions.
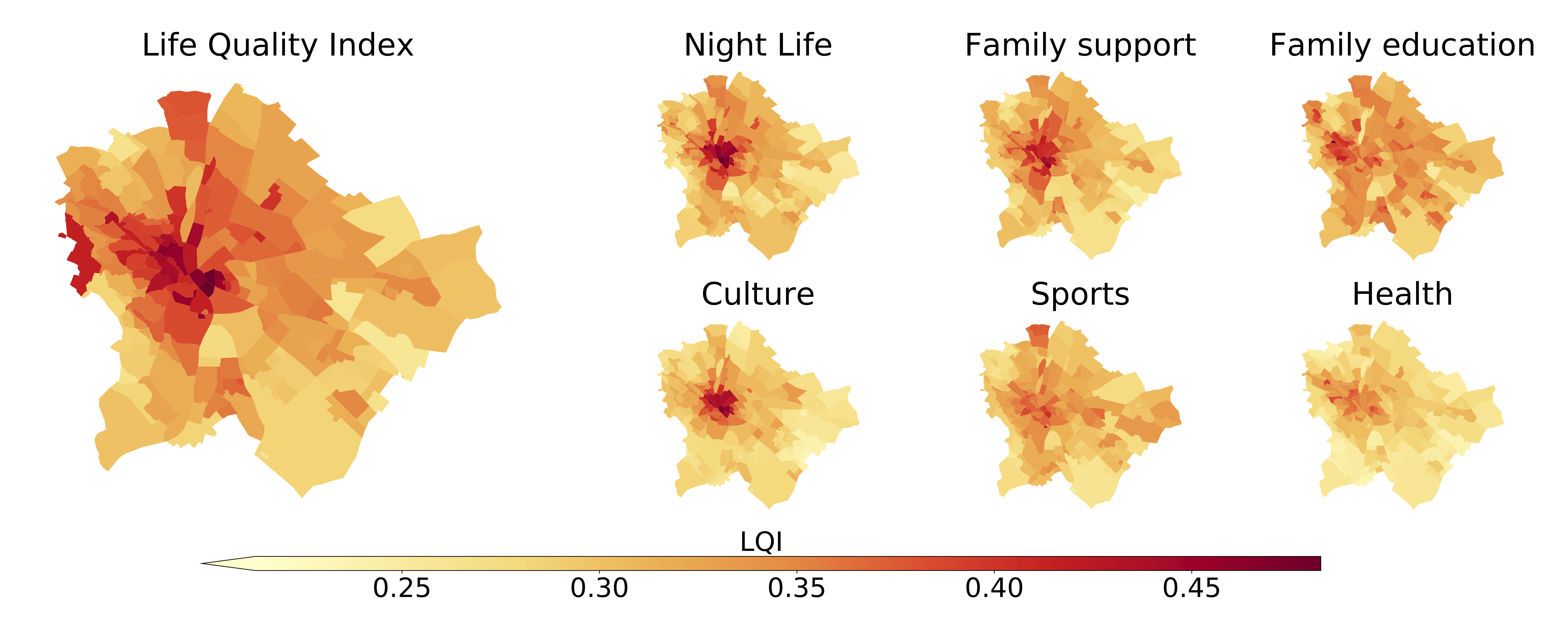
Project Overview
Developed for the municipality of Budapest, this project creates a data-driven, network-based Life Quality Index (LQI) that quantifies urban liveability through walkability and access to amenities. Using OpenStreetMap data and OSMnx Python library, the methodology assigns points of interest to nearest network nodes and applies graph-Voronoi tessellation to generate high-resolution quality landscapes. The analysis evaluates six amenity categories: family friendliness, healthcare, culture, nightlife, environment, and public safety. The study revealed how less liveable neighborhoods consistently lack amenities across categories, primarily in suburban areas with longer walking distances. These findings were used to plan targeted interventions across the underserved neighborhoods.
Key Features
Technologies
Built with Python and OSMnx for OpenStreetMap network analysis. Uses primal graph representation where intersections are nodes and sidewalks are edges. The methodology enables urban planners to identify service gaps and target interventions based on objective, data-driven walkability metrics combined with comprehensive amenity accessibility measurements.